Drone Auto-Drive Code Challenge Report¶
Introduction¶
This an online Code Challenge, the purpose is to write an “auto-pilot” program to fly a drone vehicle and successfully deliver as many packages as possible while avoiding crashing. The code challenge is licensed not to be distributed, so I am only going to describe my approach here.
Implementation¶
When I first read the code challenge description, I had two plans for implementing the auto pilot algorithm. These two methods are machine learning based auto-pilot and analytical auto-pilot algorithms.
For machine learning method, I am planning to pass all telemetry data into reinforcement learning algorithm and let the training finish the rest of the algorithm. After carefully reading the project description, I found that this idea is not valid. According to the requirents, the only information our auto-pilot algorithm getting is telemetry_packet, which includes vehicle location, wind vector, time stamp, and lidar information. We are not getting delivered message and crash message to evaluate the score of the test flight.
The second method is the analytical method. This algorithm generally include telemetry pakcet parser, command packet maker, lidar infomation explaner, tree/pad logger, smart auto-pilot algorithm, and PID controller.
Figure 1 shows the overall system diagram. The vehicle will pass telemetry pakcet to the auto-pilot algorihtm and the auto-pilot algorithm will return command packet to control the speed of the vehicle on the Y-axis. Here I leave a backdoor for humans to intervene the pilot process in case of the emergency situations. The manual control will also benefit the debugging process.
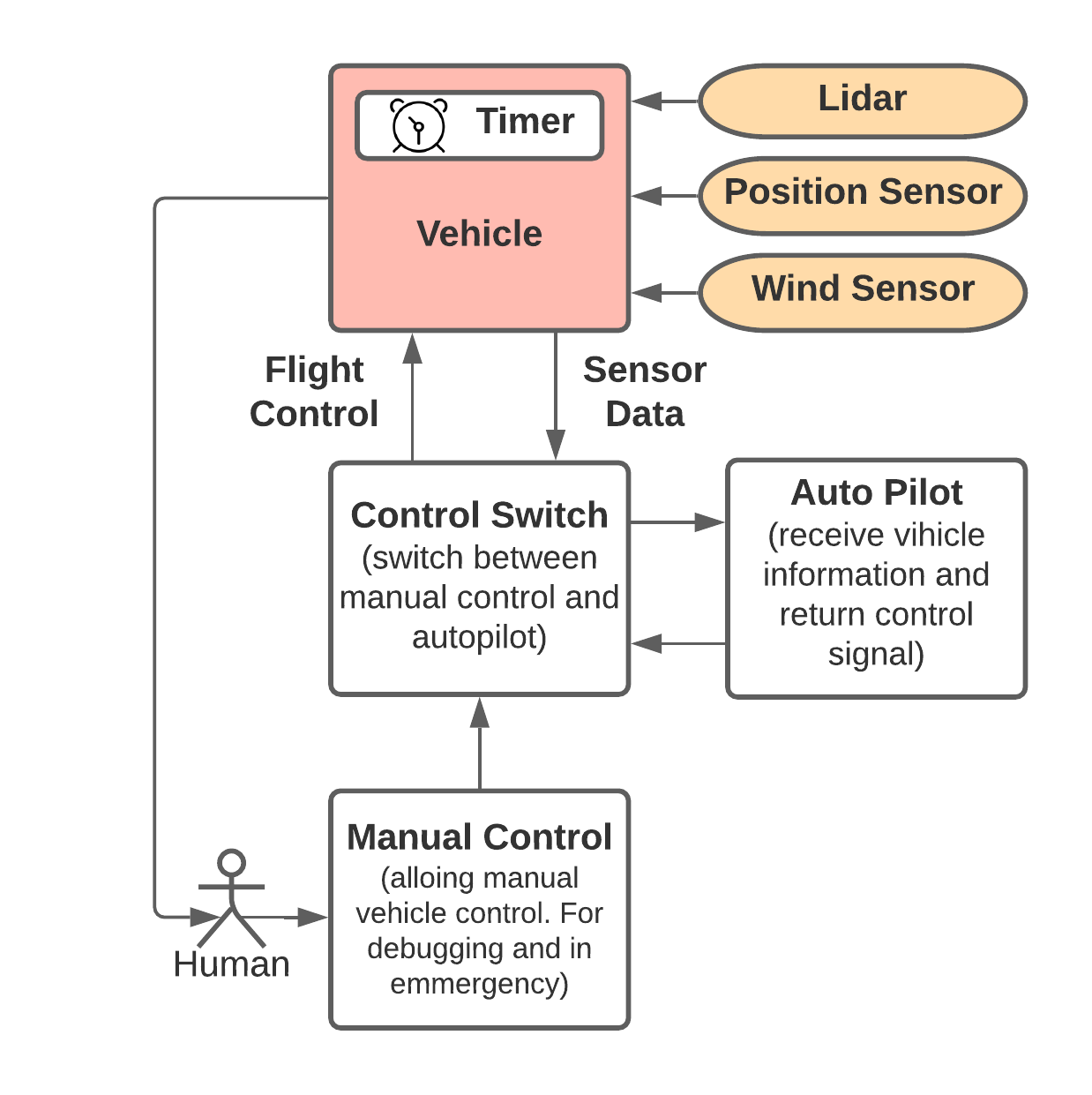
Figure 1. Overall System Diagram.¶
Figure 2 shows the auto-pilot algorithm block diagram.
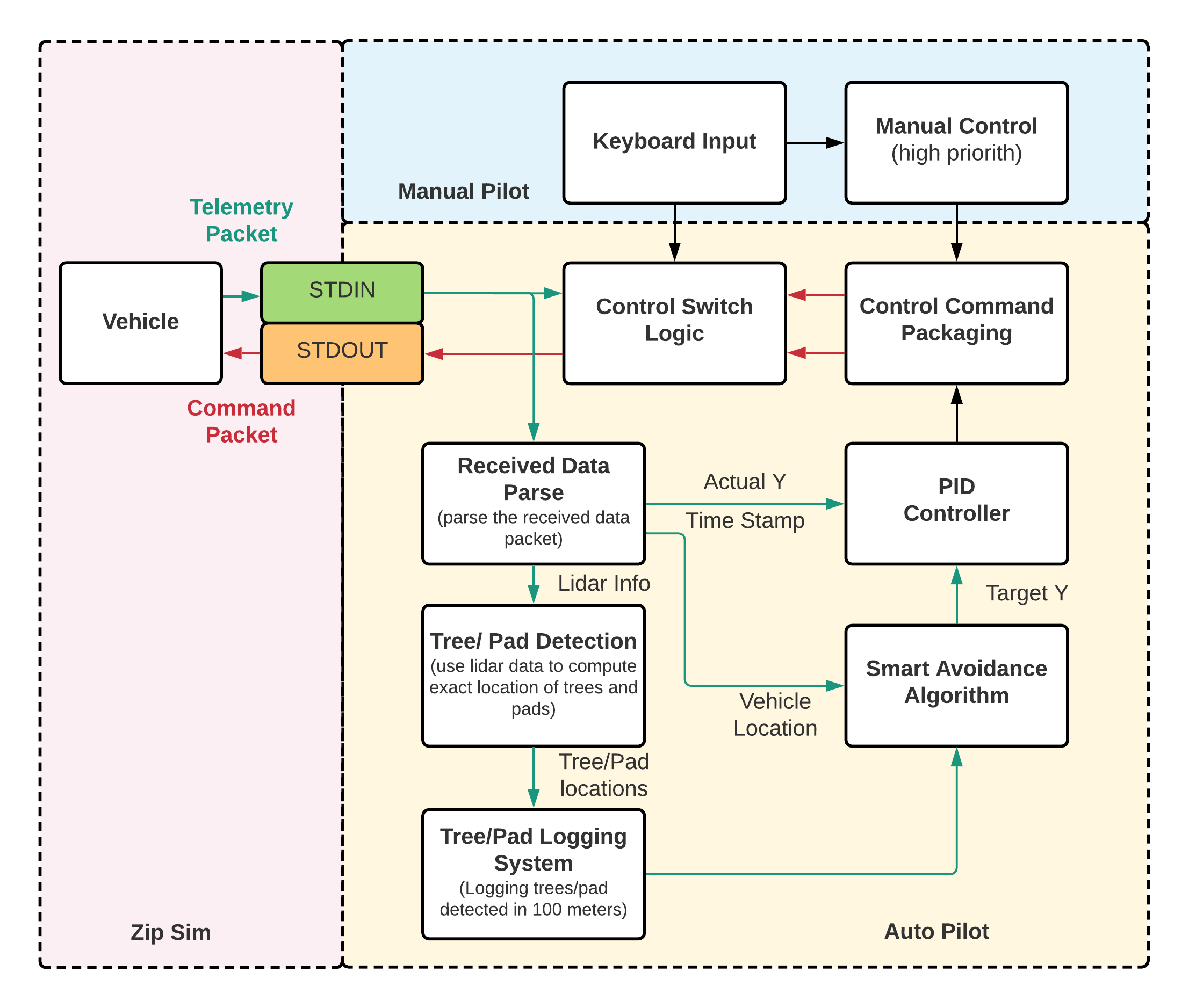
Figure 2. Auto Pilot Algorithm Block Diagram.¶
Figure 3 shows the block diagram of the PID controller for the vehicle position control.
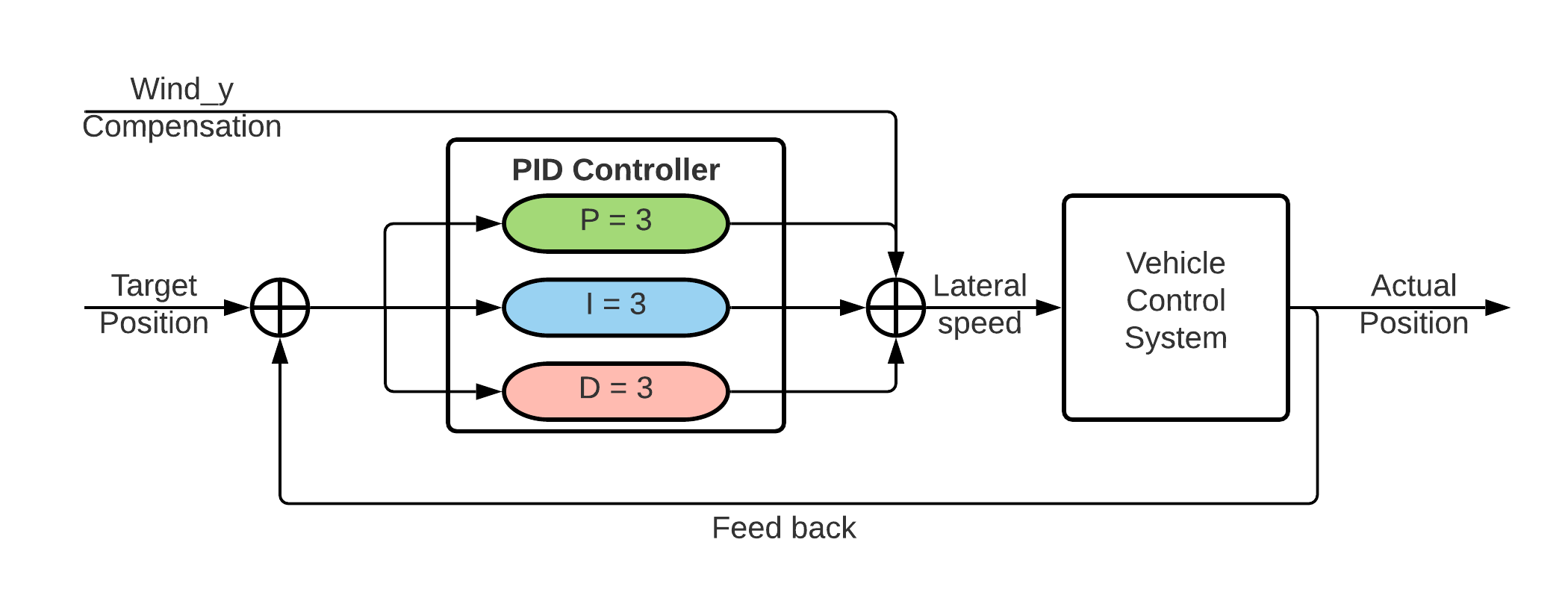
Figure 3. PID Controller Diagram.¶
Figure 4 shows how trees can be found with lidar. After compuates the tree offsets compared with the vehicle location, we can compute the absolute positions of the trees. The trees will be logged until we pass it. Once it enters the range of alert, we will mark it on the 1D map grid.
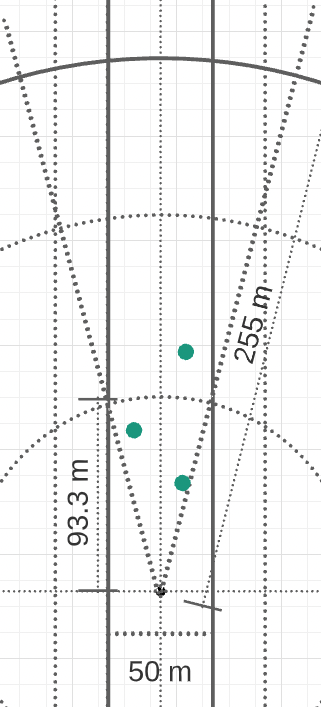
Figure 4. Lidar Converage.¶
Results¶
Figure 5 shows that the algorith can precisely detect the trees and pads according to the diameters, and mark them on the 1D map in my system.
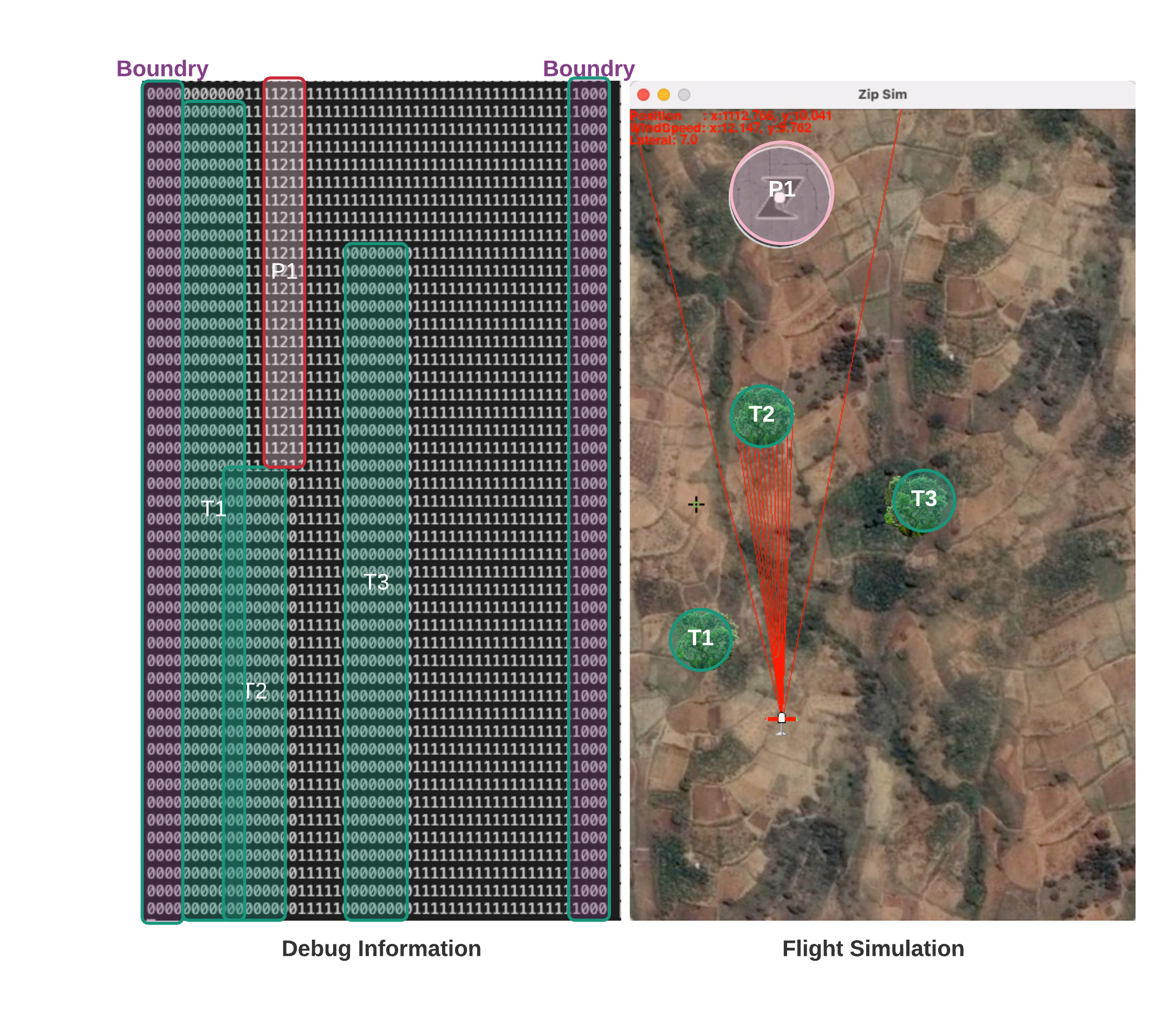
Figure 5. Simulation Result.¶
Simulation result shows that among 1000 flights, the number of ZIPAA vilolation is 7 times, the delivery rate is 58.49%, and the crash rate is 22.7%. I think this can be improved if I fine ajust the parameters. Due to the time limit, I will leave it as it is for now. The crashes are mostly caused by trees blocked by trees, by changing the margins of the flight, we can reduce the crash rate.